Graphic/GnuPlot
<app>Gnuplot</app> est un logiciel qui sert à produire des représentations graphiques en deux ou trois dimensions de fonctions numériques ou de données. Le programme fonctionne sur de nombreux ordinateurs et systèmes d'exploitation (Linux, Windows, OS/2, etc ...) et peut envoyer les graphiques à l'écran ou dans des fichiers dans de nombreux formats.
<app>Gnuplot</app> utilise également l'algorithme de Levenberg-Marquardt pour ajuster les paramètres d'une fonction numériques sur des données expérimentales.
Le programme peut être utilisé intéractivement, et est accompagné d'une aide en ligne. L'utilisateur entre en ligne de commande des instructions qui ont pour effet de produire un tracé. Il est aussi possible d'écrire des scripts gnuplot qui, lorsqu' ils sont exécutés, génèrent un graphique.
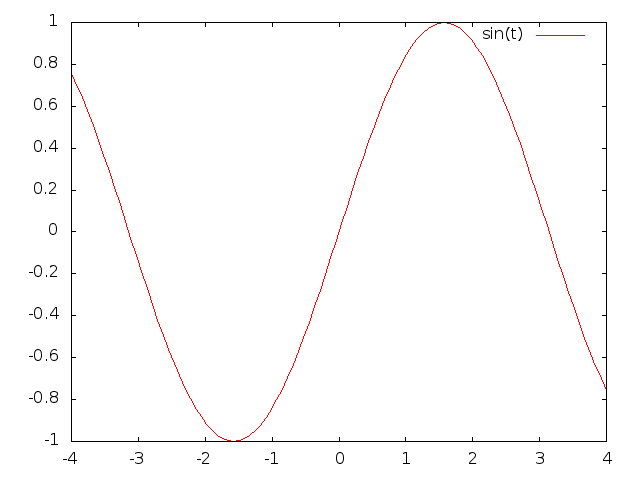
Traçage d'une fonction simple en ligne de commande
$ gnuplot gnuplot> set terminal png Terminal type set to 'png' Options are 'nocrop font /usr/share/fonts/dejavu/DejaVuSans.ttf 12 size 640,480 ' gnuplot> set output "/home/didier/tmp/gnuplot-exemple1.png" gnuplot> plot [t=-4:4] sin(t) gnuplot> quit
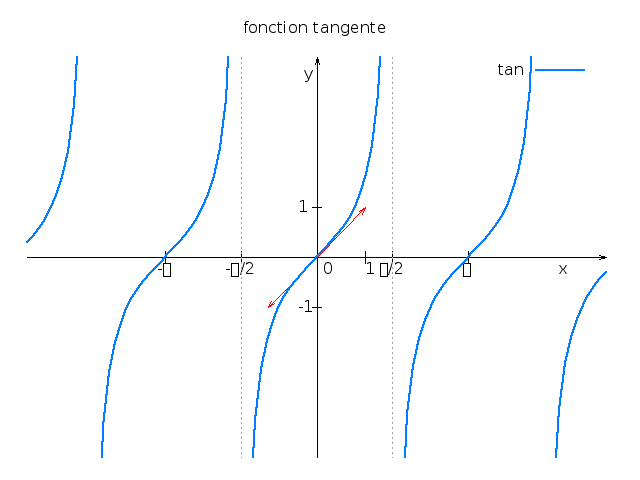
Utilisation d'un script
#définition de quelques variables
xmin=-6.
xmax=6.
ymin=-4.
ymax=4.
xdec=0.25
ydec=0.25
pasx=1.0
pasy=1.0
#initialisation du terminal
reset
set term x11
unset autoscale
set xr [xmin:xmax]
set yr [ymin:ymax]
#options
unset border
unset label
unset xtics
unset ytics
set title "fonction tangente"
#les axes
set arrow 3 from xmin,0 to xmax,0,3 lt -1 lw 0.5
set arrow 4 from 0,ymin to 0,ymax,3 lt -1 lw 0.5
#l'origine
set label "0" at xdec/2, -ydec
set label "x" at xmax - pasx, -ydec
set label "y" at -xdec, ymax - pasy/3
set label "1" at pasx, -ydec
set label "1" at -3*xdec/2, pasy
set label "-1" at -3*xdec/2, -pasy
set arrow from 1, -ydec/2 to 1, ydec/2 nohead lt -1
set arrow from 1.57, -ydec/2 to 1.57, ydec/2 nohead lt -1
set label "\34/2" at 1.57, -ydec center
set arrow from -1.57, -ydec/2 to -1.57, ydec/2 nohead lt -1
set label "-\34/2" at -1.57, -ydec center
set arrow from 3.1415, -ydec/2 to 3.1415, ydec/2 nohead lt -1
set label "\34" at 3.1415, -ydec center
set arrow from -3.1415, -ydec/2 to -3.1415, ydec/2 nohead lt -1
set label "-\34" at -3.1415, -ydec center
set arrow from 0, 0 to pasx, pasx lt 1
set arrow from 0, 0 to -pasx, -pasx lt 1
set arrow from -xdec/3, 1 to xdec/3, 1 nohead lt -1
set arrow from -xdec/3, -1 to xdec/3, -1 nohead lt -1
set arrow from -1.57, ymax to -1.57, ymin nohead lt 0
set arrow from 1.57, ymax to 1.57, ymin nohead lt 0
plot tan(x) title "tan" w l lt 3 lw 2
pause -1 "maintenant va créer un fichier au format png appuyer sur entrée"
set term png
set out "exemple2.png"
rep
set out
set term x11
pause -1 "touche entrée pour sortir"
Pour exécuter le script :
gnuplot> load 'exemple2.dat'
Utilisation de fichiers d'entrée
On peut créer un fichier ou seront stockés nos résultats de test :
- La première ligne définit les titres de colonnes*
- Les lignes suivantes présentent nos données formatées
threads test0 test1 test2 test3 test4 test5 test6 1-thread 453.95 242.34 415.96 78.12 524.16 453.21 8-threads 2959.67 807.05 2735.68 103.27 3170.74 3185.95 16-threads 5091.82 789.18 4333.02 102.65 5736.24 5794.25 24-threads 4765.96 776.50 4322.92 104.43 5315.06 5340.74 32-threads 4557.40 766.17 3775.70 104.57 4997.94 5016.92
on lance gnuplot en ligne de commande
gnuplot -e "set terminal svg enhanced size 640, 500;set style fill solid border rgb \"black\"; \
set style data histogram;set style histogram cluster gap 2;set auto x;set yrange [0:*]; \
set key on center bmargin ;set title "other-op rate";plot 'other-op.dat' using 2:xtic(1) title col, \
'' using 3:xtic(1) title col, '' using 4:xtic(1) title col, '' using 5:xtic(1) title col, \
'' using 6:xtic(1) title col, '' using 7:xtic(1) title col;"
Références
- ↑ Très bon tutoriel sur gnuplot http://www.ukonline.be/programmation/gnuplot/tutoriel